Why Task Killer is not healthy for your (Android) Phone?
In Software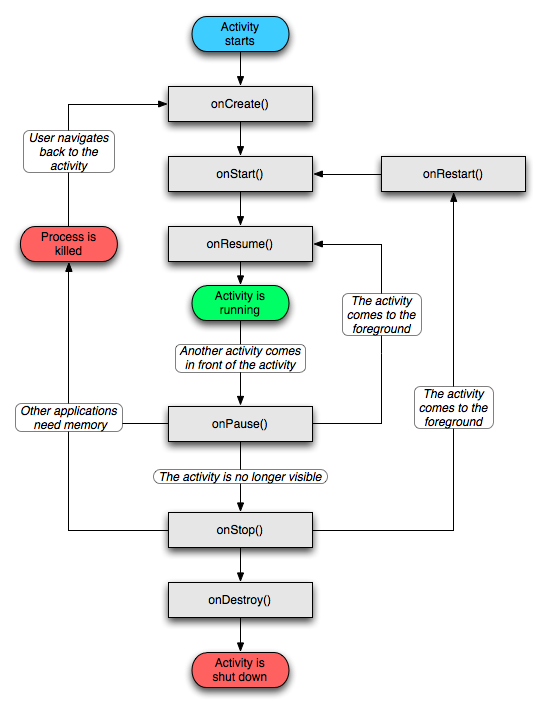 By default, every application runs in its own Linux process. Android starts the process when any of the application’s code needs to be executed, and shuts down the process when it’s no longer needed and system resources are required by other applications.
By default, every application runs in its own Linux process. Android starts the process when any of the application’s code needs to be executed, and shuts down the process when it’s no longer needed and system resources are required by other applications.
A content provider is active only while it’s responding to a request from a ContentResolver. And a broadcast receiver is active only while it’s responding to a broadcast message. So there’s no need to explicitly shut down these components.
Activities, on the other hand, provide the user interface. They’re in a long-running conversation with the user and may remain active, even when idle, as long as the conversation continues. Similarly, services may also remain running for a long time. So Android has methods to shut down activities and services in an orderly way:
An activity can be shut down by calling its finish() method. One activity can shut down another activity (one it started with startActivityForResult()) by calling finishActivity().
A service can be stopped by calling its stopSelf() method, or by calling Context.stopService().
Components might also be shut down by the system when they are no longer being used or when Android must reclaim memory for more active components.
If the user leaves a task for a long time, the system clears the task of all activities except the root activity. When the user returns to the task again, it’s as the user left it, except that only the initial activity is present. The idea is that, after a time, users will likely have abandoned what they were doing before and are returning to the task to begin something new.
There is no need for an app to do the task of killing processes in the memory since, the processes staying in memory doesn’t use battery, but killing the apps takes up CPU and hence battery.

